Diagnosis, Treatment & Surveillance Services of Ovarian Cysts
- Full Gynae examination
- Pelvic ultrasound (Trans-Abdomen/Trans-Vaginal)
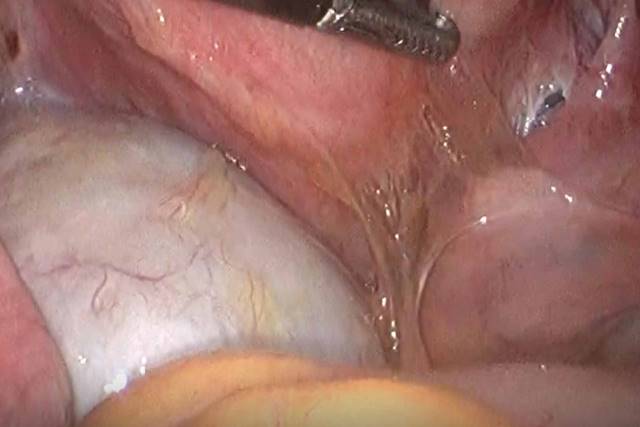
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
- Laparoscopic Surgery (Key hole removal of cyst)
Laparotomy and removal of cyst (Open surgery)
Long term surveillance of ovarian cysts
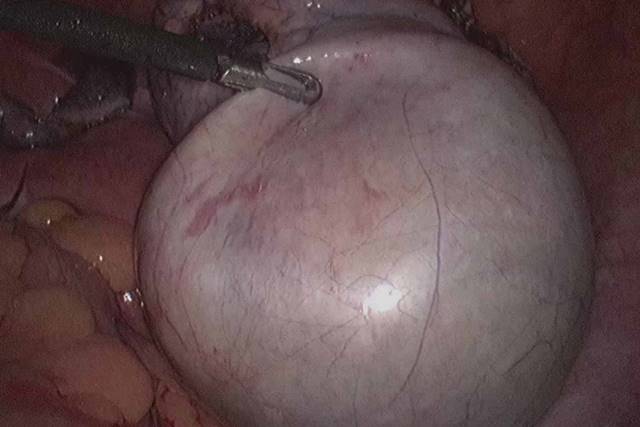
What are ovarian cysts?
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac. They can form anywhere in the body. Ovarian cysts form in or on the ovaries. The most common type of ovarian cyst is a functional cyst.
Functional cysts often form during the menstrual cycle. The two types are:
Follicle cysts.
These cysts form when the sac doesn’t break open to release the egg. Then the sac keeps growing. This type of cyst most often goes away in 1 to 3 months.
Corpus luteum cysts.
These cysts form if the sac doesn’t dissolve. Instead, the sac seals off after the egg is released. Then fluid builds up inside. Most of these cysts go away after a few weeks. They can grow to almost 4 inches. They may bleed or twist the ovary and cause pain. They are rarely cancerous. Some drugs used to cause ovulation, such as Clomid® can raise the risk of getting these cysts.
Other types of ovarian cysts are:
Endometriomas .
These cysts form in women who have endometriosis (EN-doh-MEE-tree-OH-suhss). This problem occurs when tissue that looks and acts like the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. The tissue may attach to the ovary and form a growth. These cysts can be painful during sex and during your period.
Cystadenomas.
These cysts form from cells on the outer surface of the ovary. They are often filled with a watery fluid or thick, sticky gel. They can become large and cause pain.
Dermoid cysts.
These cysts contain many types of cells. They may be filled with hair, teeth, and other tissues that become part of the cyst. They can become large and cause pain.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts?
Many ovarian cysts don’t cause symptoms. Others can cause:
- Pressure, swelling, or pain in the abdomen
- Pelvic pain
- Dull ache in the lower back and thighs
- Problems passing urine completely
- Pain during sex
- Weight gain
- Pain during your period
- Abnormal bleeding
- Nausea or vomiting
- Breast tenderness
What is the danger of ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts of more than 5 cm if left untreated or without a proper surveillance it may get complicated. The complications include:
- It get twisted causing severe abdominal pain
- It may rupture causing peritonitis
- It may bleed into the cyst, causing it to grow in size dramatically
- It may change into cancerous
- If complications occur, EMERGENCY SURGERY is required